It is difficult to achieve carbon neutrality solely by optimizing the current production processes in the building ceramic and sanitaryware industry, which calls for a fundamental change. Among the various low-carbon technologies available, the utilization of clean energy is considered one of the most fundamental, direct, and effective approaches to reducing carbon emissions. As a crucial element of the national energy strategic plan for achieving green and low-carbon development in energy consumption terminals, the utilization of ammonia-hydrogen fuel has become a focal point for the building ceramic and sanitaryware industry, domestically and internationally.
Hydrogen is an ideal clean energy source with high heat value, high energy conversion efficiency, non-toxicity, renewability, and sustainability. It offers advantages such as carbon-free combustion and a wide combustion limit range. Domestic and international equipment companies have significantly progressed in developing and utilizing hydrogen-fired kilns. However, when it comes to the large-scale application in the ceramic industry, other than sourcing and cost, there are challenges, including high energy consumption during the preparation process, high costs associated with safe storage and transportation, and significant technical requirement.
Compared to hydrogen, ammonia can be easily liquefied under low pressure at -33°C. The energy density of liquid ammonia is higher than liquid hydrogen, and the energy density of ammonia is nearly twice that of hydrogen, making it more energy-efficient for transportation and storage. In terms of cost, the production cost of ammonia is slightly higher than that of hydrogen. However, the overall cost of ammonia, including transportation and storage costs, is significantly lower. The storage cost of ammonia for 15 days is 50% lower than that of hydrogen, and the storage cost of ammonia for 182 days is even 80% lower.
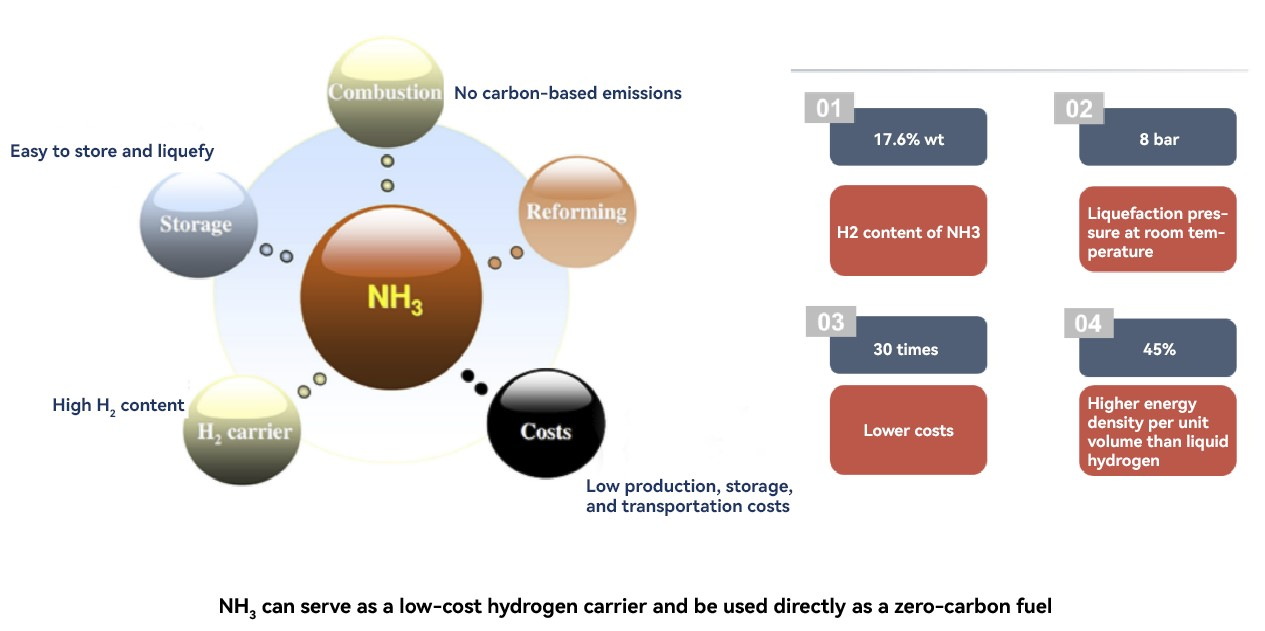
In summary, ammonia is an extremely promising clean energy carrier and zero-carbon fuel. However, research on employing ammonia as a low-carbon fuel is still in the early stages worldwide, focusing on small-scale laboratory investigations. The feasibility of using ammonia as a large-scale, low-carbon fuel in the ceramics industry has yet to be established. This situation not persisted until the end of 2022 when the " Advanced Zero-Carbon Combustion Technology Joint Innovation and Research Center" (referred to as the "Research Center"), established by Foshan Xianhu Laboratory, DLT Technology (a subsidiary of KEDA Industrial), and Oceano Ceramics, successfully designed and developed new industrial combustors capable of utilizing both pure ammonia and natural gas-ammonia mixtures, achieving stable ignition, ammonia blending, and pure ammonia combustion in DLT Technology's experimental furnaces. The team also established a comprehensive set of safety usage protocols and emergency measures specifically tailored for ammonia-fueled ceramic kilns, encompassing critical aspects such as operational procedures, ammonia storage, and transportation.
Building upon these achievements, the team completed the transformation of a 30-meter-long roller kiln at Oceano Ceramics. Originally fueled by natural gas, this kiln was converted to operate on pure ammonia and pure ammonia and natural gas-ammonia mixtures. In December 2022, the world's first green ceramic tile was successfully produced using pure ammonia fuel.
Given the current limitation to producing ammonia using renewable energy, it is not feasible to completely replace natural gas in the short term. Therefore, a hybrid combustion approach in ceramic kilns is a more practical direction to reduce carbon dioxide emissions during the ceramic firing stage. However, to implement ammonia blending, the following issues need to be addressed:
I Stable Combustion of Ammonia
Compared to the primary components of natural gas, methane and hydrogen, ammonia as a direct fuel source exhibits the following characteristics: firstly, ammonia has a lower heating value, measuring around 3000 kcal/m³; secondly, ammonia demonstrates a slower maximum laminar combustion velocity, which is only about one-fifth of that of natural gas; thirdly, ammonia has a narrow combustion limit range of 0.63-1.40, so it possesses good stability and is less prone to ignition and explosion. The primary challenge to be addressed is achieving fast and stable combustion.
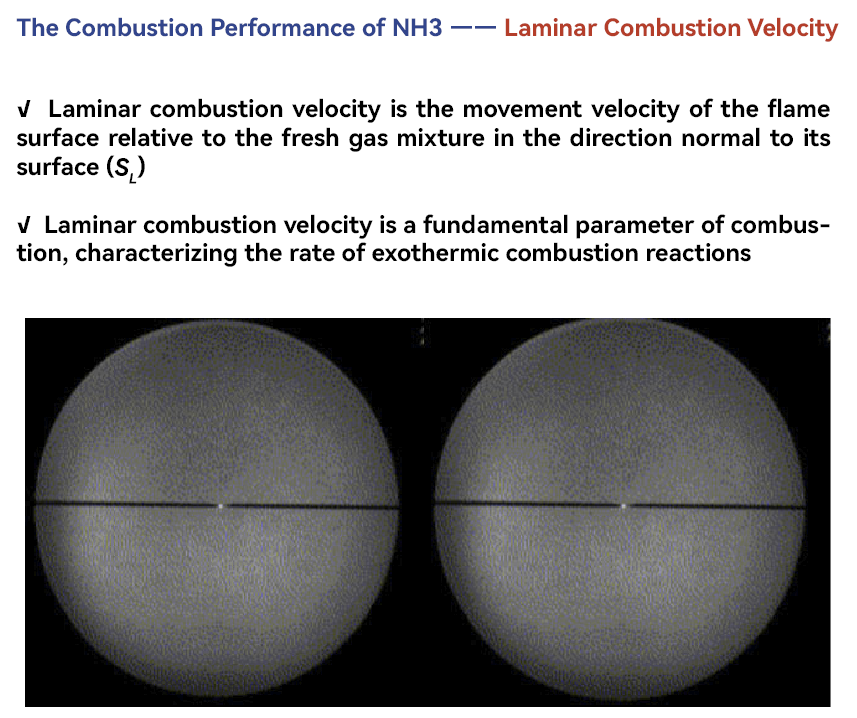
The research center team has systematically designed and optimized the entire system, from gas supply to pipeline transportation and gas nozzle, effectively addressing the technical challenges of ignition difficulty and unstable combustion flame in industrial-grade kilns using pure ammonia fuel. As a result, they have achieved highly efficient and stable combustion of pure ammonia fuel, with an efficiency above 99.9% and residual ammonia concentration below 5 ppm.

II Oxyntride Emmisions
Nitrogen oxide emissions still challenge the application of ammonia as a direct energy source. However, the research center team has developed several patented technologies that effectively reduce nitrogen oxide emissions in combustion flue gas. These technologies have undergone third-party verification, which confirms that the nitrogen oxide emissions are well below the requirements set by national standards in China.
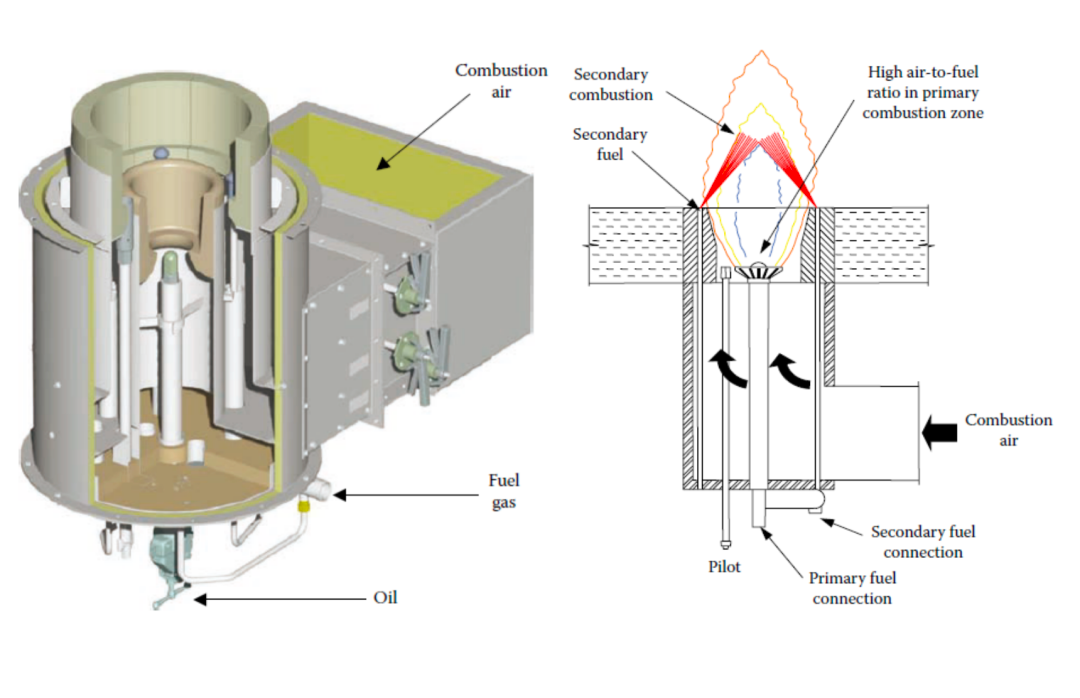
III Sources and Costs of NH3
Currently, in China, ammonia production relies primarily on coal as the main raw material, leading to significant energy consumption and high carbon dioxide emissions. Continuous research and development of "green" ammonia technology is necessary for ammonia fuel to be widely adopted. According to statistics provided by www.cheminsight.net,as of February this year, nearly 50 green ammonia projects have commenced nationwide, with a total production capacity exceeding 8 million tons. However, there is still a considerable gap to fulfill the large-scale green ammonia production required for industrial combustion. Furthermore, based on current market prices, using ammonia as an industrial fuel costs approximately twice as much as using natural gas, which is unaffordable for many companies.
There is increasing focus on the development of the green ammonia industry. Policies such as the "Guidelines for the Implementation of Energy Saving and Carbon Reduction Transformation and Upgrading in Key Areas of High Energy-consuming Industries (2022 Edition)" jointly issued by four ministries, the "14th Five-Year Plan for New Energy Storage Development" from the National Energy Administration, and the "Carbon Peaking Plan for Industrial Sectors" from the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology were introduced to address the storage and application of green ammonia. Since 2022, the development of green ammonia in China has significantly accelerated, accompanied by further implementation of these policies. The issues around the source and cost of green ammonia are expected to be resolved in the future.
As for the next strategic development of low-carbon hydrogen and ammonia technology, the research center will utilize the technological achievements in building ceramics to facilitate the transformation of large-scale production lines, allowing the actual industrial application of the ammonia-hydrogen low-carbon combustion technology. Following successful implementation, the research center will continuously promote these advancements in the industry.
KEDA Industrial Group has long consistently embraced the green and low-carbon development trend within the ceramic industry. It has innovated and integrated the principles of low-carbon, energy-saving, green, and environmental protection into its technological advancements and strategically positioned itself in the research and development of ammonia-hydrogen low-carbon combustion technology. Under its subsidiaries, Foshan KEDA Industrial and ICF & Welko, extensive research has been conducted on hydrogen hybrid combustion technology, resulting in the development and engineering applications of hydrogen-powered, high-efficiency, energy-saving wide-body roller kilns. Furthermore, KEDAIndustrial Group's subsidiary, HLT China, has achieved significant breakthroughs in the application of ammonia and successfully produced the world's first green ceramic tile using pure ammonia fuel. Through its commitment to innovative and sustainable technologies, KEDA Industrial Group has emerged as a prominent force driving sustainable development within the industry and paved the way for the achievement of carbon peaking and carbon neutrality in the ceramic and other building material industries, making significant contributions to the sustainable development of China’s ceramic industry.
(Written by China Building Ceramic & Sanitaryware Association)




 loading...
loading... 03 Aug 2023
03 Aug 2023